Expert Advice
Terms like angiography and angioplasty come up often when discussing heart condition diagnosis and treatments. Both crucial cardiovascular procedures, they serve distinct purposes: Angiography is a diagnostic test, and angioplasty is a treatment. This comprehensive guide will dive into what these procedures entail, their differences, associated risks, recovery time, and costs.
Angiography is an imaging technique that is used to visualise the inside of our blood vessels and organs, particularly arteries and veins. This procedure is commonly performed to detect blockages or abnormalities in the heart, brain, and other vital areas.
The angiography procedure uses a special dye and X-rays. A catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, typically in the groin or arm, and guided to the area to be examined. The dye injected through the catheter highlights the blood vessels on X-rays, allowing doctors to spot any issues, such as blockages.
Doctors typically recommend an angiography test when a patient shows symptoms of a cardiovascular condition, like shortness of breath, chest pain or numbness in limbs. It is also performed before certain surgeries to provide detailed imaging of blood vessels.
Main types of angiography include:
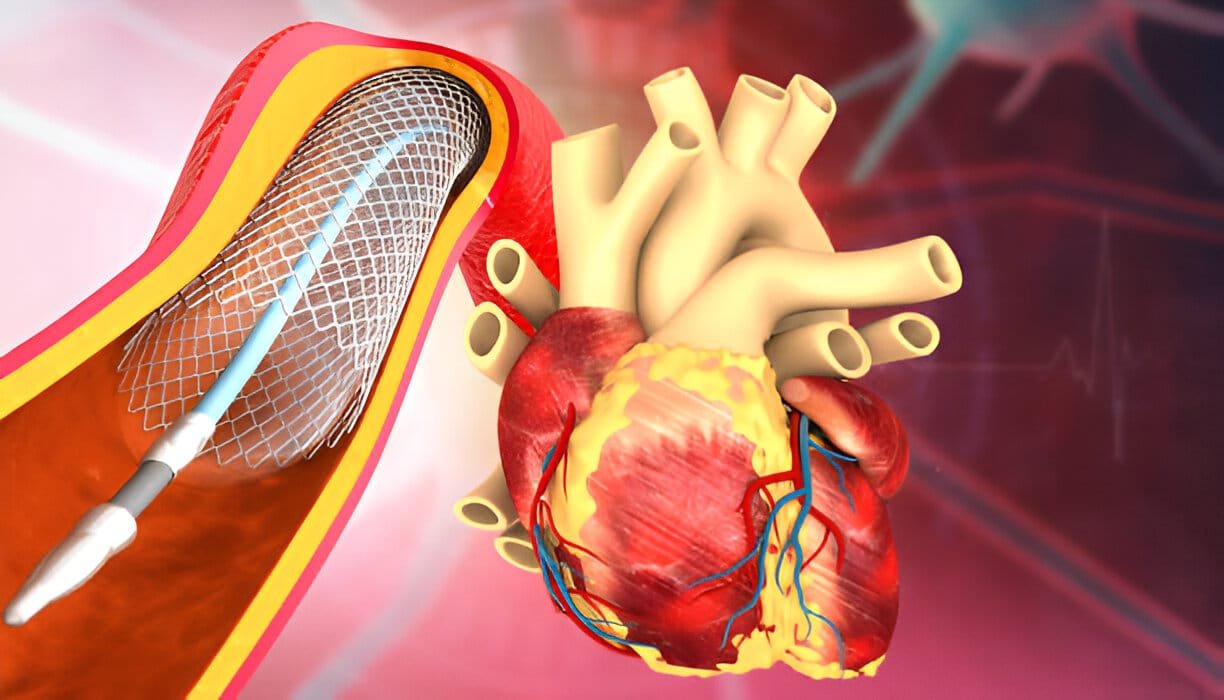
Angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure that aids in restoring blood flow in blocked or narrowed arteries. Unlike angiography, which is diagnostic, angioplasty is a treatment.
During angioplasty surgery, a balloon-tipped catheter is guided to the blocked artery. The balloon is then inflated to compress the plaque against the artery walls, widening the artery. In many cases, a stent (a small wire mesh tube) is placedc that helps keeping the artery open.
Doctors recommend angioplasty when medications or lifestyle changes fail to relieve symptoms such as severe chest pain (angina) or when there is a high risk of a heart attack.
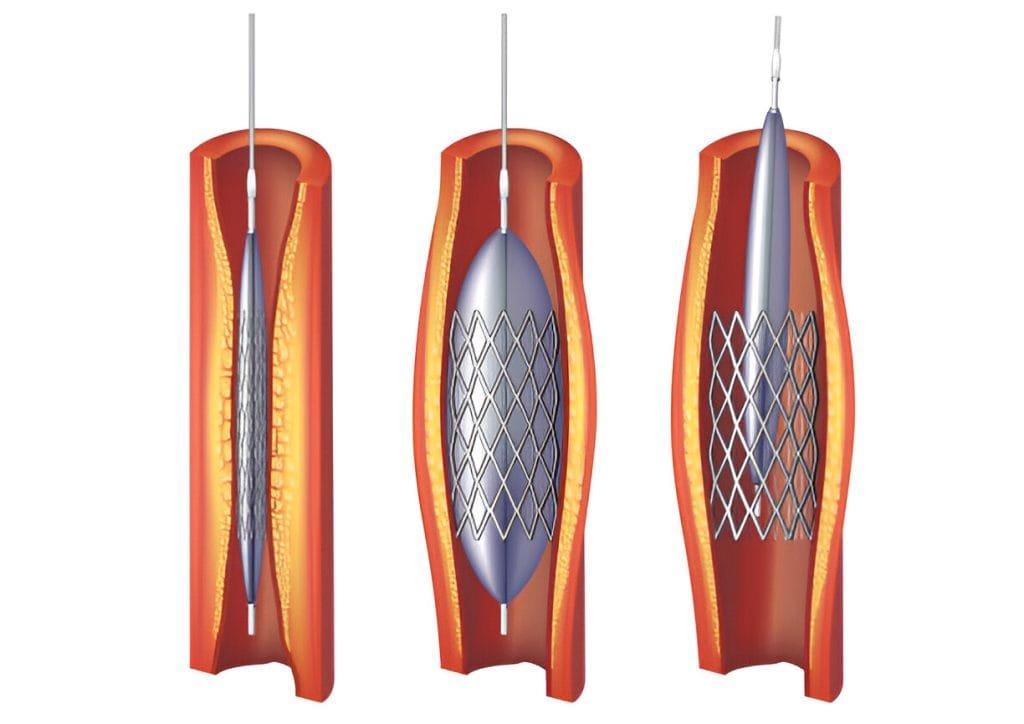
Main types of angioplasty include:
While Angiography and angioplasty are closely related but serve distinct purposes in cardiovascular care:
It is important to understand the risks of both the procedures. They are as follows:
While angiography is generally safe, it carries some risks:
Angioplasty risks of death are extremely low, but some complications may occur, such as:
Both procedures involve relatively short recovery periods, but they differ in intensity:
After an angiography test, patients are usually observed for a few hours and can return to normal activities within 24-48 hours. Minor discomfort at the catheter site is common.
Recovery time after angioplasty surgery is slightly longer. Patients may need to stay in the hospital overnight for monitoring. They might also be advised to avoid heavy activities for a week. Regular check ups and follow ups are also essential to ensure full recovery.
The angiography cost in India varies depending on various factors like the hospital and region. Typically, the price ranges from ₹8,000 to ₹25,000.
Angioplasty, is a more complex procedure, and hence is more expensive. The angioplasty cost in India, ranges between ₹1,50,000 and ₹3,00,000.
Understanding the difference between angiography and angioplasty is important when in comes to cardiovascular care. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of heart disease, consult Atrius Cardiac Care. Early diagnosis and timely intervention is essential for both cases.
Discover world-class cardiac care at Atrius Cardiac Centre, where advanced technology meets compassionate expertise. Our team of specialists are dedicated to provide you the best of heart health facilities, offering you personalised treatments.
Take the first step toward a healthier heart—schedule your appointment with Atrius Cardiac Care today.